
In the early 1900s, a culture of people that lived in Micronesia called the YAP, used a form of money called Rai stone. These big circular stones could get pretty massive and weigh up to four tons. Not something the average person could carry in a wallet! Instead, they documented who owned any part of the Rai stones.
One day, sailors were transporting a large Rai stone that fell off their vessel and sank to the bottom of the sea. Upon telling the YAP, they said, “Well okay, we know that you had it, and it still exists, so it’s still valuable.” The Yapese then documented and added its value to their list of traded currencies. Even though the stone was at the bottom of the sea, and couldn’t be seen or touched, it was still part of the Yap’s economy.
We Decide What Money Looks Like
Money is about the exchanges that we have with each other. If we say that gold is valuable, it is. Cocoa beans, stones, and plants have all represented forms of currency in human history.
Today, Rai stones are still a part of the Yap’s economy. Unusual? Not really. Consider that most of our money is digitally documented, traded and exchanged without any paper money or coins exchanging hands. It’s an unseen value.
What is Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, are digital currencies. The world of cryptocurrency is based on specialized mathematics called cryptography. Cryptography is the study of secret or secured communication. A cryptographer searches for, and creates code with two very important things in mind:
• highlighting information so that it can be visible in very plain sight
• verifying a piece of information’s source.
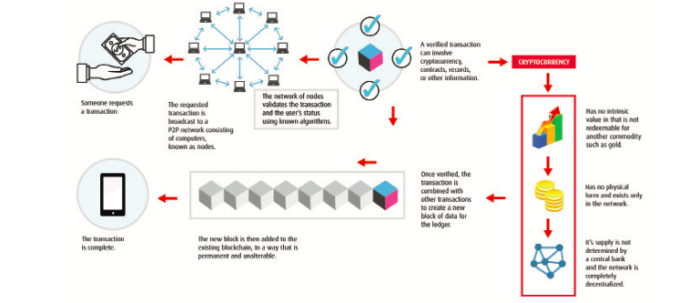
How is cryptocurrency tracked?
Blockchain. Think of blockchain as a giant sheet of internet paper called a ledger, that records transactions. Anyone who makes a transaction gets their own sheet of paper with a record of all the other transactions being made. Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be changed or hacked.
All who transact can see and access the ledger, but nobody – no banks or institutions – can control it. Because blockchain is a ledger system for currency, it can track value of work by artists, musicians, and writers. It can also verify the source of a transaction or “ownership.” This is important where corrupt governments have been known to steal land from people. Paper documents or “deeds” for purchase of land can be torn or burned to destroy proof of ownership. A blockchain transaction of land transfer is secure. In many ways, blockchain can keep accountability and fairness in check.
Just like the Internet changed the way we communicate, programmable money – like cryptocurrency – will change the way we pay and decide on value.
Where Does Bitcoin Come From?
Miners. In the same way we mine for gold, we mine for cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency miners are computer users who look for “wins.” A win is when a very hard digital puzzle is solved by a computer. It’s sort of like hitting a jackpot: imagine if a series of dice were rolled and they all landed on the same number. Miners use high powered computers that find and identify a highlighted “fact or truth” about a particular block of information. When this is discovered by the miner, it’s a win and a crypto coin is earned.
Bitcoin was created in 2009 and today, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have financial value. Bitcoin is being used in restaurants and for purchases in more places because people – not banks and governments – have decided that cryptocurrency has value. That is pretty cool.
Visit our website for more content or to subscribe!

